

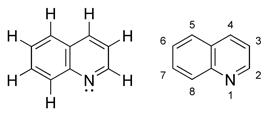
Quinoline (1-azanaftalen, 1-benzazin, benzo-piridin) is an aromatic organic compound, and it has a heterocyclic structure.
The chemilcal formula of it is : C9H7N.
This colorless hydroscopic liquid has a piercingly strong odor. Exposed to sunlight for a longer period of time,
it will turn yellow later brown.
It dissolves well in organic solvents, but not so well in cold water.
Quinoline is created in the processiong of paint and other metallurgical products.
It is mainly used in preservatives. It can also be used as a disinfectant or as a solvent and in the production of medicine, in yellow
medicines it is used as paint.
Quinoline is a toxic chemical, interferencing with human body it irritates the nostrils.
Long term effects are not known, but tests show, that it damages the liver.
Quinoline can be extracted from coal tar, and it can be found in oil shale.
It can be produced as follows:
1. With Doebner-Miller reaction using anilines and unsaturated carbonyl compounds
2. Friedländer synthesis using 2-aminobenzaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
3. Skraup synthesis using ferrous sulfate, glycerol, aniline, nitrobenzene, and sulfuric acid.
4. Povarov reaction using an aniline, a benzaldehyde and an activated alkene.
The melting point of quinoline is -15 °C and its densitiy is 1,09 g/ml.
Articles
Quinoline has other names. The other names of Quinoline are the following: 1-azanaphthalene, benzo[b]pyridine, 1-benzazine, benzazine, benzazabenzene, benzopyridine, 1-benzine, quinolin, chinoline, chinoleine, chinolin, leucol, leukol, leucoline.
A quinoline and that isomer a isoquinoline as well, is like an oil, colorless, strong smell liquid.
Compound and that isomer properties are following:
| Properties |
Quinoline | Isoquinoline |
| Melting-point | -15°C – 5 F | 26-28°C – 78.8-82.4 F |
| Boiling-point | 238°C – 460.4 | 242°C – 467.6 F |
| Density | 1,09 g/ml | 1,099 g/ml |
A quinoline is yellow first, then turns brown when exposed to light.
In water quinoline is only slightly soluble but is in organic solvents well soluble.